Glossary
2D Pixel Arrays - An array of pixels tiled in two directions.
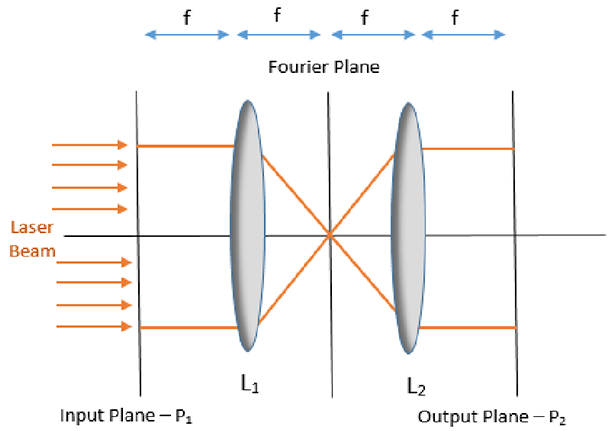
4F System - A common arrangement for optical filtering. This system has 2x Fourier setups, which are arranged serially. (See Fourier setup). An input image is transformed by the first Fourier setup to the spatial frequency domain and typically subjected to an optical filter. The filtered image is reconstructed by the second Fourier setup.
Active Ribbons - Ribbons connected with the CMOS driver. The number of CMOS drivers corresponds to the channels of the module. We can control their displacement by the CMOS driver.
AM / Additive Manufacturing - One of the technologies of 3D printing.
AMP Mode / Amplitude Mode - In amplitude mode the modulator data is a higher resolution amplitude value with all pixel transitions occurring at the same fixed delay after the column trigger. In delay mode the modulator data contains an amplitude value and delay value so that each pixel transition can be delayed from the column trigger independently.
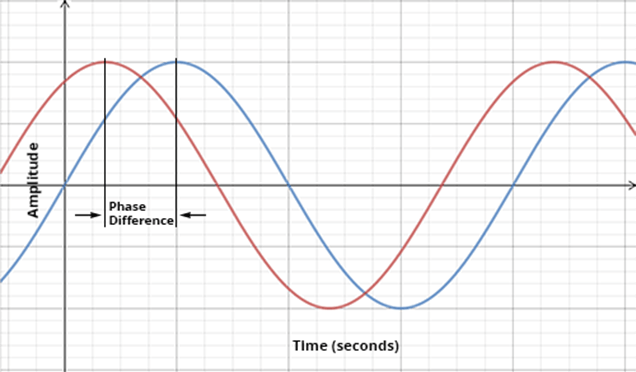
Amplitude - See figure. Light is an electromagnetic wave. It represents the sinusoidal signal. Amplitude is the magnitude of the light wave and phase specifies the location or timing of a point within a wave cycle of a repetitive waveform.
Aperture - A hole or an opening that primarily limits light propagated through the optical system.
Attenuate - To decrease the light intensity by the GLV/PLV modulator.
B1 format - B1 is one of paper sizes defined by the JIS (Japanese Industrial Standard) P0202. B1 paper’s dimensions are 728 x 1030 mm (28.6 × 40.6 in). B1 format is also defined by ISO 216, but it is a little smaller, 707 x 1000mm.
Bias Ribbons - Ribbons connected to the bias electrode. FLV device arranges active ribbon and bias ribbon neighboring each other. All the bias ribbons are connected to one electrode.
Bit-Depth - How many bits for controlling voltage to actuate ribbon or faceplate. For example, ten bits has 1024 steps to apply voltage.
CMOS Drivers / Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Drivers - Various kinds of small electronic devices are made using CMOS technology. A CMOS driver applies voltage on SLM’s MEMS device based on a digital input signal. Each channel of the MEMS device is assigned to its own CMOS driver.
Coplanar - In the same plane or at the same z-height (depth).
Cosmo Controller - Product name of the predetermined data controller board for GLV/PLV products.
CTP / Computer to Plate - A direct imaging system for constructing printing plates using a laser. Published image data on a computer is sent to the system which writes the image onto a printing plate.
Cylindrical - Having a cylindrical shape or profile. A cylindrical lens usually has a feature that cuts a cylinder glass rod with a plane parallel to the cylinder’s rotation axis.
DPM (TM) - Displacement phase modulator.
DOE / Diffractive Optical Element - A DOE has micro-structured surface relief patterns designed for a specific light diffraction response. A DOE can control light propagation in various ways. A common example of a DOE is a Fresnel lens.
DW3000 - Product name of a SCREEN’s direct imaging system for semiconductor wafer.
Etendue - A property of light relating spatial and angular extent that is preserved through a lossless optical system. Typically evaluated for illumination systems, higher etendue has a larger divergence angle or larger light source area while low etendue systems require the tight focus achievable using a laser.
FPD / Flat Panel Display - Viewing technology on a flat screen.
Fourier Setup - An optical setup to get a Fourier transform image. “Fourier” comes from “Fourier transform,” a mathematical operation that is used in signal processing and optics. When an object is placed on the front focal plane of the lens and illuminates the object with a plane wave, the Fourier transform image (spatial frequency distribution of the object) appears on the back focal plane of the lens.
Fraunhofer Diffraction - Also known as far-field diffraction. As light propagates from the object, the light intensity distribution is changed. When the distance is far enough from the object, we call the location far-field and can treat the light propagation as Fraunhofer diffraction. If the object is illuminated with a plane wave, a Fourier transformed image appears at the field.
Fresnel Diffraction - Also known as near-field diffraction. Similar to the previous definition, when the distance from the object is not far, the location is referred to as near-field and can treat the light propagation as Fresnel diffraction.
FTL / Fourier Transform Lens - A lens being used in a Fourier transform configuration.
Galvo Scanner - A device used to rapidly and precisely move a mirror or other optical element to control the direction and position of a laser beam.
Gamma [Response] - A gamma or gamma correction is a curve relating luminance to some value. The "gamma response of the eye" refers to the non-linear way humans perceive brightness, meaning one is more sensitive to changes in darker areas than in brighter areas.
Gaussian [Beam] - Ideal intensity profile of a laser beam. The profile has Gaussian distribution. Gaussian beams are fundamental in laser systems because they can be efficiently focused and manipulated.
GLV / Grating Light Valve - Ribbon-based spatial light modulator from SLM.
LeVina - Product name of a SCREEN’s direct imaging system. LeVina is for the advanced packaging market.
Linearized - Modify nonlinear response of reflected light intensity or displacement of the piston to linear response against input digital signal by CMOS driver architecture.
MEMS / Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems - Devices with microscopic features that combine mechanical and electrical properties.
Modulators - A device that varies one or more properties of a signal.
Module - A final packaged and integrated MEMS device including driver electronics.
Monochromatic - When describing a light source, monochromatic light has a narrow wavelength spectrum, typically from a laser.
Multimode - When describing a light source, the light propagates in multiple spatial modes resulting in a broader beam than a single-mode source.
NIR / Near Infrared - Infrared is invisible light beyond red. The range of NIR wavelengths is approximately 700 nm to 2500 nm.
PCIe / Peripheral Component Interconnect Express - A high-speed interface standard used to connect components.
Phase Modulation - See definition of Amplitude. Phase modulation means to control the phase of light waves.
Platesetter - Another name for CTP.
PLV / Planar Light Valve - A two dimensional equivalent of a one-dimensional GLV.
Powell Lens - A special type of lens to create a top hat beam shape.
PWM / Pulse-Width Modulation - A technique used to control the average power delivered to a load by varying the width of pulses in a periodic waveform.
Quiescent - State of the device with no voltage applied to it.
Shack–Hartmann - Special optical sensor’s name. This sensor is for measuring the wavefront distribution of light.
SiGe / Silicon Germanium - A common semiconductor processing film.
SiN / Silicon Nitride - A common semiconductor processing film.
UV / Ultra-Violet - Invisible light beyond violet. The range of the wavelength of UV is 100 nm to 400 nm.
UV-NIR Wavelengths - Range of wavelengths from ultra-violet to near-infrared. SLM’s products have operating wavelengths ranging from 350 nm to 1100 nm.
UVDI / Ultra-Violet Direct Imaging - The use of ultraviolet light to create images or patterns onto a surface.
No terms found.